Personal finance activities for high school students include budgeting exercises and understanding credit. These activities build essential financial skills.
Teaching personal finance to high school students is crucial. Early financial education helps them make informed decisions. Students learn to manage money, budget, and save. Understanding credit and debt prepares them for future financial responsibilities. Schools can incorporate real-life scenarios to make lessons engaging.
Interactive activities like mock stock trading and budgeting projects boost interest. Financial literacy games and apps also make learning fun. Encouraging discussions about money management helps students feel more comfortable with financial topics. By mastering these skills, students gain confidence and financial independence. Early education sets the foundation for a secure financial future.
Introduction To Personal Finance
Personal finance is how you manage your money. It includes saving, spending, and investing. Learning about personal finance helps high school students make smart money choices. This knowledge is key for their future success.
Importance For Teens
Teens need to learn about money management early. Understanding finance helps them avoid debt. It also teaches them to save for big goals. These skills are important for adult life.
Early Financial Education
Early financial education sets a solid foundation. High school is the perfect time for this. It is easier to form good habits young. Students can learn through fun activities and real-life scenarios.
| Activity | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Budgeting Exercises | Teaches money management |
| Savings Challenges | Encourages saving habits |
| Investing Games | Introduces investment concepts |
These activities make learning fun. They also provide real-life lessons. Students gain confidence in managing their money.
Budgeting Basics
Learning about budgeting is essential for high school students. It helps them manage their money wisely. They can save for future goals and avoid unnecessary debt. Let’s dive into the basic steps of budgeting.
Creating A Budget
Creating a budget is the first step. Start by listing all sources of income. This can include allowances, part-time job earnings, or gifts. Next, list all monthly expenses. These could be school supplies, snacks, or transportation costs.
Here is a simple table to illustrate:
| Income | Amount |
|---|---|
| Allowance | $50 |
| Part-time Job | $100 |
| Total Income | $150 |
| Expenses | Amount |
|---|---|
| School Supplies | $30 |
| Snacks | $20 |
| Transportation | $15 |
| Total Expenses | $65 |
Subtract total expenses from total income. The result is your savings. In this example, the savings would be $85.
Tracking Expenses
Tracking expenses is vital to stick to your budget. Use a notebook or a budgeting app. Record every penny spent. This helps in identifying spending patterns.
Here are some tips for tracking expenses:
- Keep all receipts.
- Update your expense tracker daily.
- Review your spending weekly.
By following these steps, students can manage their money better. They will learn valuable skills for their future financial well-being.
Saving Strategies
Teaching high school students about saving strategies is essential. Understanding how to save money helps them make wise decisions. These skills will benefit them for a lifetime. Let’s explore some effective saving strategies for teens.
Setting Savings Goals
Setting savings goals is a critical first step. Goals help students stay focused. Here are some simple steps for setting savings goals:
- Identify what to save for (e.g., a new phone or college).
- Determine how much money is needed.
- Set a realistic timeframe to save the amount.
For instance, if a student wants to buy a $300 phone in six months, they need to save $50 each month. Breaking it down makes the goal manageable.
Building An Emergency Fund
An emergency fund is money set aside for unexpected expenses. Teaching teens to build an emergency fund prepares them for life’s surprises. Here’s how to start:
- Decide on an emergency fund goal (e.g., $500).
- Set aside a small amount regularly (e.g., $5 weekly).
- Keep the fund in a separate account to avoid spending it.
Below is a simple table to illustrate how small savings add up:
| Week | Amount Saved | Total Savings |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | $5 | $5 |
| 2 | $5 | $10 |
| 3 | $5 | $15 |
| 4 | $5 | $20 |
After 20 weeks, the student will have saved $100. This method teaches consistency and patience.
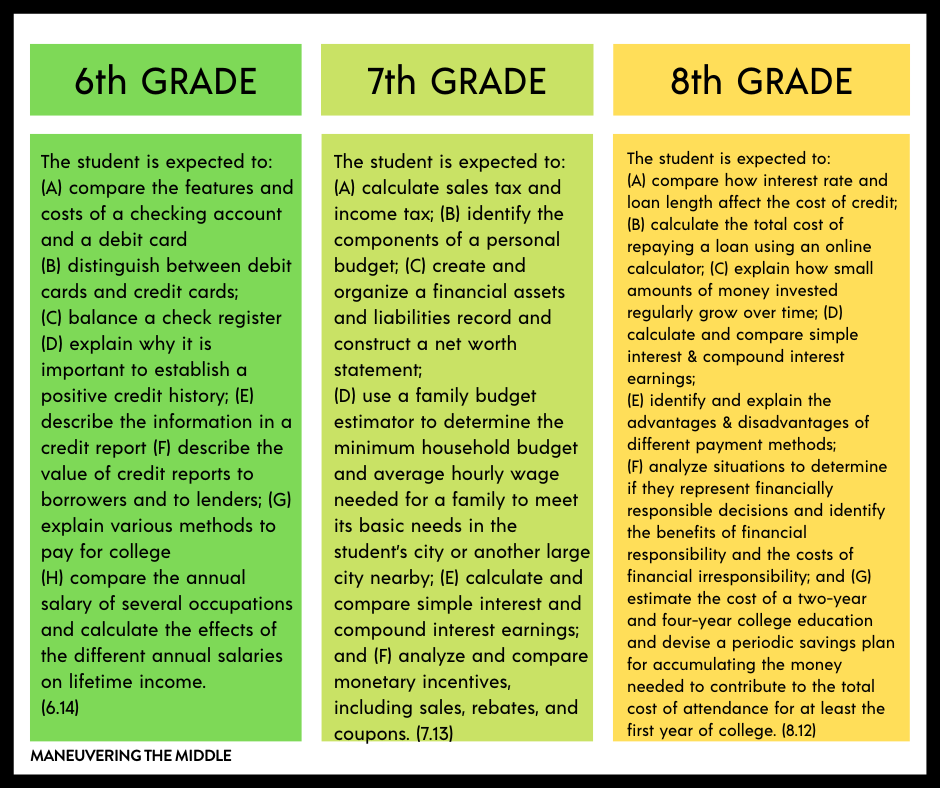
Credit: www.maneuveringthemiddle.com
Understanding Credit
Understanding credit is essential for high school students. It sets the foundation for their financial future. Good credit can help secure loans and lower interest rates. Bad credit can limit opportunities and increase costs. Let’s dive into the basics of credit scores and credit cards.
Credit Scores
A credit score is a number that represents your creditworthiness. It ranges from 300 to 850. Higher scores mean better credit. Here are the key factors that affect your credit score:
| Factor | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Payment History | 35% |
| Amounts Owed | 30% |
| Length of Credit History | 15% |
| New Credit | 10% |
| Types of Credit Used | 10% |
Payment history is the most important factor. Always pay your bills on time. Amounts owed is the second most important. Try to keep your balances low.
Credit Cards
Credit cards are a common way to build credit. They let you borrow money up to a limit. You must pay back what you borrow. Here are some key points about credit cards:
- Interest Rates: Credit cards charge interest on unpaid balances.
- Credit Limit: This is the maximum amount you can borrow.
- Minimum Payment: The least amount you must pay each month.
- Fees: Some cards have annual fees, late fees, or other charges.
Use credit cards wisely. Only charge what you can pay off each month. This helps build a strong credit history. Avoid carrying a balance to prevent high interest charges.
Smart Spending
Learning how to manage money is crucial for high school students. Smart spending habits help students save money and make wise financial decisions. This section will discuss how students can develop these habits.
Needs Vs. Wants
Understanding the difference between needs and wants is essential. Needs are things you must have to live, like food and shelter. Wants are things you would like to have but can live without.
- Needs:
- Food
- Clothing
- Shelter
- Healthcare
- Wants:
- Video games
- Concert tickets
- Designer clothes
- Luxury items
High school students should prioritize needs over wants. This helps them manage their money better.
Making Informed Purchases
Students should research before buying anything. This includes comparing prices and reading reviews.
- Set a budget: Determine how much you can spend.
- Research: Look up different products and compare prices.
- Read Reviews: Check what others say about the product.
- Make a Decision: Choose the best product within your budget.
Using these steps helps students avoid impulse buys and save money. Smart spending leads to better financial health in the future.

Credit: nearpod.com
Investing Fundamentals
Learning about investing is crucial for high school students. It helps them understand how to grow their money over time. This section covers the basics of investing, focusing on stocks and long-term investments.
Introduction To Stocks
Stocks represent ownership in a company. When you buy a stock, you own a part of that company. The value of stocks can change daily. This change depends on the company’s performance and market conditions.
Investing in stocks can be risky. But it can also offer high returns. It’s important to research before buying stocks. Look at the company’s history, performance, and future plans.
Here are some key points about stocks:
- Stocks can be bought and sold on stock exchanges.
- Stock prices can go up or down.
- Investing in stocks requires careful research.
Long-term Investment
Long-term investments are held for several years. They are less risky compared to short-term investments. Long-term investments help build wealth over time.
Benefits of long-term investing:
- Potential for higher returns.
- Less impact from market fluctuations.
- Compounding interest benefits.
Types of long-term investments include:
- Stocks
- Bonds
- Mutual funds
- Real estate
It’s important to start investing early. Even small amounts can grow significantly over time. Consistent investing can lead to substantial wealth.
Managing Debt

Managing debt is a crucial skill for high school students. Understanding debt helps students make smart financial decisions early in life. This section covers different types of debt and how to manage them effectively.
Types Of Debt
There are various types of debt that students should be aware of. These include student loans, credit card debt, and personal loans.
- Student Loans: These are loans taken to pay for education expenses.
- Credit Card Debt: This is the debt accumulated through credit card use.
- Personal Loans: These are loans borrowed for personal use, like buying a car.
Debt Repayment Plans
Creating a debt repayment plan is essential for managing debt. Here are some common strategies:
- Snowball Method: Pay off the smallest debts first. This helps build momentum.
- Avalanche Method: Focus on paying off debts with the highest interest rates first. This saves money on interest.
- Debt Consolidation: Combine multiple debts into one loan with a lower interest rate.
Below is a table comparing these methods:
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Snowball Method | Quick wins, easy to stay motivated | May pay more in interest |
| Avalanche Method | Save on interest | May take longer to see progress |
| Debt Consolidation | Single payment, lower interest | Requires good credit score |
Understanding these strategies helps students manage their debt effectively. This builds a solid foundation for their financial future.
Financial Tools And Resources
High school students can benefit greatly from learning personal finance. Using the right tools and resources makes this easier. Here are some key financial tools and resources for students.
Budgeting Apps
Budgeting apps help students manage their money. These apps show income and expenses in one place. Below are some popular budgeting apps:
- Mint: Tracks expenses, creates budgets, and offers financial tips.
- You Need a Budget (YNAB): Helps students allocate every dollar with ease.
- Goodbudget: Uses the envelope method for budgeting.
These apps are user-friendly and available on both iOS and Android devices.
Educational Websites
Educational websites offer valuable information on personal finance. These websites teach students about saving, investing, and more. Here are some top educational websites:
- Investopedia: Offers articles, tutorials, and quizzes on financial topics.
- Khan Academy: Features free courses on economics and personal finance.
- Practical Money Skills: Provides games, lessons, and resources for students.
These websites are free and accessible from any device with internet access.
| Tool | Description | Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Mint | Tracks expenses and offers budgeting tips. | iOS, Android |
| YNAB | Helps allocate every dollar with ease. | iOS, Android |
| Goodbudget | Uses the envelope method for budgeting. | iOS, Android |
Parental Involvement
Teaching personal finance to high school students is crucial. Parents play a big role in this. Their involvement can make a huge difference. By engaging in finance activities, parents can guide their teens better.
Role Of Parents
Parents should be role models for their teens. Teens watch and learn from their parents. When parents practice good financial habits, teens notice. This helps teens understand the importance of managing money.
Parents can help in setting up a budget. They can show teens how to track expenses. This can be a fun activity. Use apps or simple notebooks. Tracking expenses helps in understanding where money goes.
Parents can also teach about saving. Open a savings account for your teen. Encourage them to save a part of their allowance. This teaches the value of saving early.
Family Financial Discussions
Having family financial discussions is vital. Make money talks a regular habit. Include teens in these talks. This helps them learn from real-life examples.
Discuss monthly expenses and bills. Show how to manage household finances. Talk about how to prioritize needs over wants. This helps teens understand the difference.
Use a table to discuss family budget:
| Category | Monthly Budget |
|---|---|
| Groceries | $500 |
| Utilities | $150 |
| Entertainment | $100 |
Discuss financial goals with teens. This can be saving for college or a new gadget. Setting goals helps in planning and motivation.
Parents should discuss credit and debt. Explain the difference between good and bad debt. Show how credit cards work. This can prevent future financial mistakes.
Make these discussions interactive. Ask questions. Encourage teens to share their views. This makes learning about finance fun and engaging.

Credit: www.pnwfcu.org
Frequently Asked Questions
How To Teach High Schoolers About Finances?
Teach high schoolers about finances through practical lessons, budgeting exercises, and real-life examples. Use interactive tools and apps. Discuss saving, investing, and managing debt. Invite financial experts for guest lectures. Encourage questions and discussions for better understanding.
What Are The Five 5 Areas Of Personal Finance?
The five areas of personal finance are income, spending, saving, investing, and protection. Effective management of these areas ensures financial stability and growth. Each area plays a crucial role in achieving financial goals and security. Balancing these elements helps in maintaining a healthy financial life.
How To Make Financial Literacy Fun?
Use games, apps, and interactive challenges to teach financial concepts. Incorporate real-life scenarios and rewards to engage learners.
What Are The 5 Main Categories Of Personal Finance?
The 5 main categories of personal finance are income, savings, investments, spending, and protection. Managing these helps achieve financial stability.
Conclusion
Teaching personal finance to high school students equips them with essential life skills. It fosters financial responsibility and smart decision-making. Early financial education can lead to better money management in adulthood. Encourage students to engage in budgeting, saving, and investing activities.
Empowering youth with financial knowledge is a step toward a secure future.

