To read a credit report, start by reviewing personal information for accuracy. Next, examine credit accounts, payment history, and inquiries.
Understanding how to read a credit report is essential for managing your financial health. A credit report provides a detailed record of your credit history and helps lenders assess your creditworthiness. Begin by checking your personal details, such as name, address, and Social Security number, to ensure accuracy.
Then, review your credit accounts, including credit cards, loans, and mortgages, noting any discrepancies. Pay close attention to payment history, as timely payments boost your credit score. Finally, examine the inquiries section to see who has accessed your credit information. Regularly monitoring your credit report helps you spot errors and protect against identity theft.
Credit: www.thelpa.com
Obtaining Your Credit Report
Obtaining your credit report is the first step to understanding your financial health. A credit report provides detailed information about your credit history. This helps you identify any errors and take corrective measures.
Where To Get It
You can get your credit report from major credit bureaus like Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion. These agencies provide free annual reports. You can request them online through the Annual Credit Report website. You may also contact them directly by phone or mail.
Frequency Of Access
It’s important to check your credit report regularly. You are entitled to one free report from each bureau every year. This means you can access a free report every four months if you stagger your requests. Reviewing your report multiple times a year helps you spot errors early. Frequent checks also help in monitoring for signs of identity theft.
Consider setting reminders on your calendar. This ensures you do not miss the opportunity to review your credit report.
Basic Structure Of A Credit Report
Understanding the basic structure of a credit report is crucial. It helps you manage your finances. A credit report is divided into several sections. Each section provides different types of information.
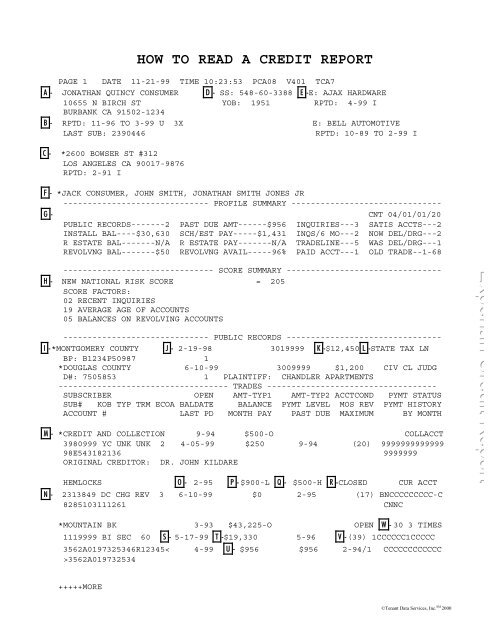
Personal Information
The first section is Personal Information. It includes details like:
- Name
- Address
- Social Security Number
- Date of Birth
- Employment Information
This section helps identify you. Ensure this information is accurate. Mistakes here can affect your credit score.
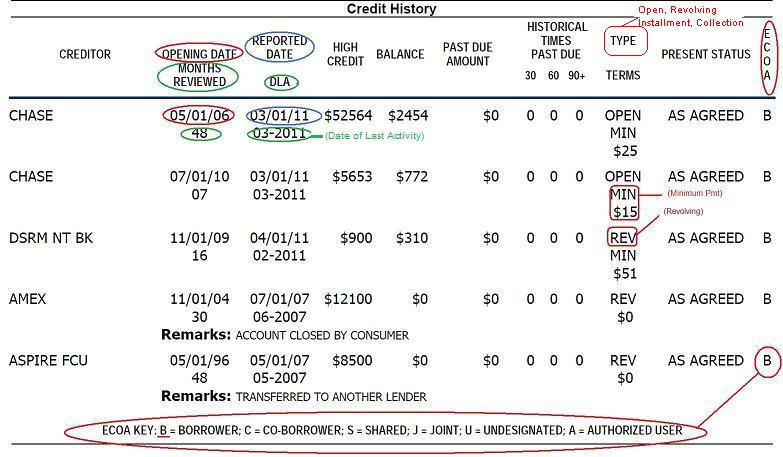
Account Summary
The next section is the Account Summary. This part lists your credit accounts. It shows:
| Account Type | Account Status | Credit Limit | Balance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Credit Card | Open | $5,000 | $1,200 |
| Auto Loan | Closed | $20,000 | $0 |
This section helps you track your debts. It shows if your accounts are in good standing. Review this section regularly.
These sections form the core of your credit report. They provide a snapshot of your financial health. Understanding them is the first step in managing your credit effectively.
Understanding Credit Scores
Credit scores are essential in determining your financial health. They are used by lenders to assess your creditworthiness. Knowing how to read a credit report helps you understand and improve your credit score.
Score Range
Credit scores range from 300 to 850. Each range indicates different levels of credit risk. The higher the score, the better your credit.
| Score Range | Rating |
|---|---|
| 300-579 | Poor |
| 580-669 | Fair |
| 670-739 | Good |
| 740-799 | Very Good |
| 800-850 | Excellent |
Factors Affecting Score
Several factors influence your credit score. Knowing these can help you maintain a good score.
- Payment History: Paying bills on time positively affects your score.
- Credit Utilization: Keep your credit card balances low.
- Length of Credit History: Longer credit histories improve your score.
- New Credit: Too many new accounts can lower your score.
- Credit Mix: Having different types of credit is beneficial.
Understanding these factors helps you make better financial decisions. Regularly check your credit report to ensure accuracy.
Credit: www.yumpu.com
Reading Account Details
Reading account details on a credit report is essential. It helps you understand your credit standing. This section breaks down each part of the account details.
Types Of Accounts
Your credit report lists different types of accounts. These accounts include:
- Credit Cards: These are revolving accounts.
- Mortgages: Loans for buying property.
- Auto Loans: Loans for purchasing vehicles.
- Student Loans: Loans for education expenses.
- Personal Loans: Unsecured loans for various uses.
Each account type affects your credit differently. Understanding these types helps manage your credit better.
Payment History
Payment history is crucial for your credit score. It shows how well you pay your debts. Here’s what to look for:
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| On-time Payments | Payments made by the due date. |
| Late Payments | Payments made after the due date. |
| Missed Payments | Payments not made at all. |
Always aim for on-time payments. Late or missed payments harm your credit score. Check your payment history for any errors.
To sum up, reading account details on your credit report is vital. Understand the types of accounts and keep track of your payment history. This helps you maintain a healthy credit score.
Identifying Errors

Reading a credit report can be tricky. It’s crucial to identify any errors. Errors can lower your credit score. This section will guide you on spotting mistakes.
Common Mistakes
Errors on credit reports are common. Here are some frequent mistakes:
- Incorrect Personal Information: Wrong name, address, or date of birth.
- Account Errors: Incorrect account balances or statuses.
- Duplicate Accounts: Same account listed multiple times.
- Unknown Accounts: Accounts you never opened.
- Data Management Errors: Payments marked late that were on time.
How To Dispute
Disputing errors is simple. Follow these steps:
- Gather Evidence: Collect documents that prove the error.
- Contact the Credit Bureau: Write a dispute letter.
- Submit Your Dispute: Send the letter and evidence to the bureau.
- Wait for Response: The bureau will investigate and respond.
Use a template for your dispute letter:
[Your Name]
[Your Address]
[City, State, ZIP Code]
[Date]
[Credit Bureau Name]
[Address]
[City, State, ZIP Code]
Dear [Credit Bureau Name],
I am writing to dispute the following information on my credit report. The items I am disputing are incorrect and should be removed or corrected. Please see the attached documents for proof.
[list disputed items here]
Please investigate these matters and correct the errors.
Sincerely,
[Your Name]
After sending your dispute, monitor your credit report. Ensure the errors are corrected.
Impact Of Inquiries
Understanding the impact of inquiries on your credit report is crucial. Inquiries are records of when someone checks your credit. They can affect your credit score. There are two types of inquiries: soft inquiries and hard inquiries. Knowing the difference is essential for managing your credit health.
Soft Inquiries
Soft inquiries occur when you or a business checks your credit for non-lending purposes. These inquiries do not affect your credit score. Examples include:
- Checking your own credit report
- Pre-approved credit card offers
- Background checks by employers
Soft inquiries are visible only to you. They are not shown to lenders or creditors. This means they have no negative impact on your creditworthiness.
Hard Inquiries
Hard inquiries happen when you apply for credit or a loan. These inquiries can affect your credit score. Examples include:
- Applying for a new credit card
- Mortgage applications
- Auto loan applications
Hard inquiries are visible to lenders. Too many hard inquiries in a short time can lower your score. It signals that you might be a higher credit risk.
Here is a table summarizing the key differences:
| Type of Inquiry | Visible to Lenders | Affects Credit Score |
|---|---|---|
| Soft Inquiry | No | No |
| Hard Inquiry | Yes | Yes |
Monitoring your credit report for inquiries is important. This helps you understand your credit score better.
Monitoring Your Credit
Monitoring your credit is crucial. It helps you spot errors and detect fraud early. Regular checks and using credit monitoring services can protect your financial health. This section will guide you on how to monitor your credit effectively.
Regular Checks
Regularly checking your credit report is a good habit. It keeps you informed about your financial status. You can get a free report from each of the three major credit bureaus once a year. These are:
- Equifax
- Experian
- TransUnion
Stagger your requests to get a free report every four months. This way, you can monitor your credit throughout the year. Look for any errors or suspicious activities. If you find any, report them immediately.
Credit Monitoring Services
Credit monitoring services offer another layer of protection. They notify you of any changes to your credit report. This includes new accounts, credit inquiries, or changes in your account balances. Here are some popular credit monitoring services:
- Credit Karma
- Identity Guard
- LifeLock
These services can be free or paid. Free services might offer basic monitoring. Paid services often provide more detailed reports and alerts. Choose a service that fits your needs and budget.
| Service | Free/Paid | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Credit Karma | Free | Basic monitoring, credit score updates |
| Identity Guard | Paid | Detailed reports, identity theft insurance |
| LifeLock | Paid | Comprehensive monitoring, alerts, insurance |
Using credit monitoring services can give you peace of mind. You will be alerted to any changes quickly. This helps you take action before any serious damage is done. Monitoring your credit is a step towards financial security.
Improving Your Credit
Improving your credit score is vital. It opens doors to better loan rates and financial freedom. Let’s dive into the key strategies.
Paying On Time
Paying your bills on time is crucial. It shows lenders you are reliable. Set up automatic payments. This helps avoid missed deadlines.
- Set reminders for due dates.
- Use automatic payments.
- Pay more than the minimum.
Reducing Debt
Reducing your debt improves your credit score. Keep your credit utilization low. Aim for less than 30% of your limit.
- Create a budget.
- Track your spending.
- Pay off high-interest debts first.
| Action | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Pay on time | Shows reliability |
| Reduce debt | Improves credit score |
Consistently practicing these habits will boost your credit score. Stay committed and watch your score rise.

Credit: www.lexingtonlaw.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Should You Read A Credit Report?
Read your credit report by checking personal information, account history, credit inquiries, public records, and dispute errors.
How To Interpret A Credit Score?
A credit score ranges from 300 to 850. Scores above 700 are considered good. Scores below 600 may indicate risk. Check your score regularly for accuracy. High scores can lead to better loan terms and lower interest rates. Maintain good financial habits to improve your score.
What Do The Numbers Mean On A Credit Report?
The numbers on a credit report indicate your credit score. They reflect your creditworthiness to lenders. Higher scores mean lower risk.
How To Read Credit Rating Report?
To read a credit rating report, start with the summary. Check the rating score, outlook, and key risk factors. Review detailed sections for financial analysis, historical performance, and future projections. Understand the rating scale used. Always compare with industry benchmarks.
Conclusion
Reading a credit report is essential for maintaining financial health. Understanding key sections helps identify errors and fraud. Regularly checking your report keeps you informed and proactive. Stay diligent, and take control of your financial future. By mastering these steps, you ensure better financial decisions and security.

