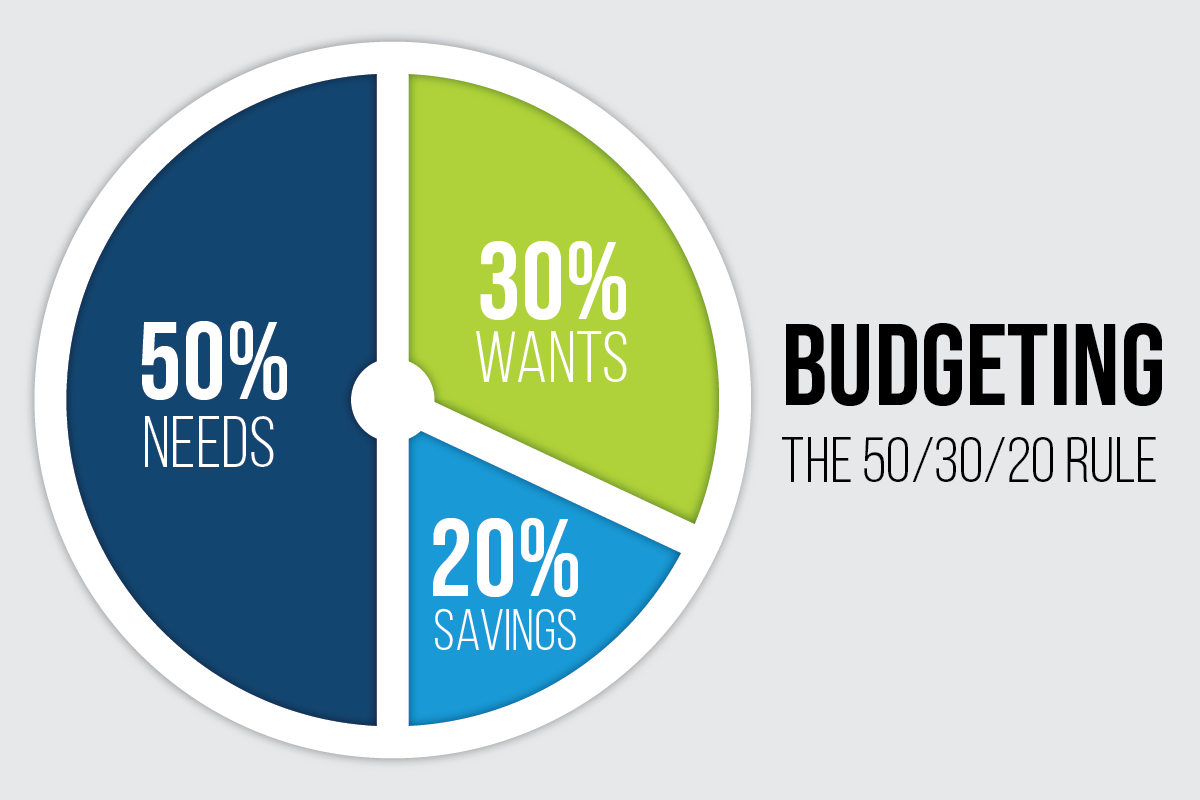
The 50/30/20 budget rule divides income into needs, wants, and savings categories, allocating 50%, 30%, and 20% respectively. It simplifies managing finances through clear, practical allocations.
Navigating the maze of personal finance can often seem daunting. Yet, the 50/30/20 budget rule offers a beacon of clarity, transforming complex budgeting into a straightforward task. This method not only guides individuals in effectively distributing their income but also in achieving a balanced financial lifestyle.
By earmarking 50% of your income for essentials like rent and groceries, 30% for personal desires such as dining out and entertainment, and the remaining 20% towards savings or debt repayment, this rule fosters a healthy financial habit. It’s a strategy that adapts to various income levels, making it a versatile tool for anyone aiming to enhance their financial wellbeing. Embracing this rule can lead to a more organized and stress-free approach to managing money, setting the foundation for a secure financial future.
Introduction To The 50/30/20 Budget Rule
Welcome to the world of savvy budgeting with the 50/30/20 Budget Rule. This simple yet effective method helps you manage your money wisely. Let’s dive into how it works and why it’s a game-changer for your finances.
Origins Of The Budgeting Strategy
The 50/30/20 Budget Rule was first introduced by Elizabeth Warren and Amelia Warren Tyagi. They shared it in their book “All Your Worth: The Ultimate Lifetime Money Plan”. Their goal was to make budgeting easy for everyone. This rule has since become a popular guide for managing personal finances.
Basic Principles Behind The Rule
The rule breaks down your after-tax income into three categories:
- 50% for needs
- 30% for wants
- 20% for savings or paying off debt
This simple division makes budgeting straightforward. You ensure that your essential needs are covered, while also setting aside money for fun and your future. Let’s see an example:
| Category | Percentage | Example (If your after-tax income is $3000) |
|---|---|---|
| Needs | 50% | $1500 (rent, utilities, groceries) |
| Wants | 30% | $900 (dining out, hobbies) |
| Savings/Debt | 20% | $600 (savings account, debt repayment) |
By following this rule, you can take control of your finances. You’ll be able to cover your essential needs, enjoy life, and save for the future. It’s a balanced approach to managing money.
Breaking Down The 50/30/20 Rule
Managing money feels easier with the 50/30/20 rule. It splits income into three parts: needs, wants, and savings. Let’s explore how this budgeting framework can work for you.
Allocating The 50%: Essential Needs
Essential needs take up half of your income. These are expenses you must pay. Think of housing, food, and utilities. Here’s a quick look:
- Rent or mortgage – A roof over your head
- Groceries – For daily meals
- Bills – Electricity, water, internet
- Transportation – Getting to work or school
- Insurance – Health, car, home
- Minimum debt payments – Credit cards, loans
The Flexible 30%: Wants And Lifestyle Choices
Wants are non-essential but add joy to life. This part of your budget is for fun and leisure. Here’s how you might use it:
| Entertainment | Movies, concerts |
|---|---|
| Dining Out | Restaurants, cafes |
| Shopping | Clothes, gadgets |
| Hobbies | Crafts, sports |
| Travel | Vacations, getaways |
Securing The Future: The 20% Savings
The last part is about building your future. Save and invest this slice of your paycheck. Aim for financial goals like retirement. Here are key areas to focus on:
- Emergency Fund – For unexpected costs
- Retirement Savings – Think long-term
- Investments – Stocks, bonds, real estate
- Debt Repayment – More than minimums
Real-world Examples
Exploring the 50/30/20 budget rule through real-world scenarios brings its effectiveness to life. Let’s dive into how this method works for different people.
Case Study: Single Professional In A City
Consider Alex, a graphic designer living in a bustling city. Earning $4,000 monthly, Alex applies the 50/30/20 rule:
- Essentials ($2,000): Rent, groceries, utilities, and transportation.
- Wants ($1,200): Dining out, subscriptions, and hobbies.
- Savings ($800): Retirement fund and emergency savings.
Alex keeps living costs low despite the high city prices. The 50/30/20 rule ensures a balanced budget.
Budget Allocation For A Family Of Four
The Smiths, a family of four, earn a combined $6,000 monthly. Their 50/30/20 budget looks like this:
| Category | Percentage | Monthly Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Essentials | 50% | $3,000 |
| Wants | 30% | $1,800 |
| Savings | 20% | $1,200 |
This structure helps the Smiths manage their home, enjoy life, and save for the future.

Credit: www.citizensbank.com
Customizing The 50/30/20 Rule
Customizing the 50/30/20 Rule lets you tailor budgeting to your life. This rule divides income into three parts. Needs get 50%, wants 30%, and savings 20%. But everyone’s finances differ. Your income, expenses, and goals shape your budget. It’s about finding the right balance. Let’s explore how to adjust this rule for different situations.
Adjustments For Higher Income Earners
High earners might need less for needs. This leaves more for savings or wants. Here’s how you can adjust:
- Reduce needs to 45% or less.
- Boost savings to 25% or more.
- Allocate extra to wants or investments.
Modifying Percentages For Financial Goals
Have big financial goals? You might want to save more. Here’s how to shift your budget:
- Identify your financial goals.
- Decide on a higher savings rate.
- Adjust needs and wants to meet this rate.
Example: Saving for a home? You might go 45/25/30.
Remember, these are just starting points. Your budget should fit your life. Change the rule as needed. Keep it simple and make it work for you.

Common Pitfalls And How To Avoid Them
The 50/30/20 budget rule is a powerful tool for managing finances. Yet, some mistakes can derail your budget plan. Understanding these pitfalls is key. Let’s explore them and learn how to stay on track.
Mistaking Wants For Needs
Identifying true needs is crucial for the 50/30/20 rule. Needs are essentials, like rent and food. Wants are extras, like eating out or the latest phone. Mixing these up can upset your budget. Here’s how to keep them straight:
- Make a list of your monthly expenses.
- Label each as a need or a want.
- Be honest with yourself.
- Adjust your spending to match the 50/30/20 plan.
Underestimating Savings Contributions
Savings are often overlooked. Yet, they are vital for financial health. The 20% savings contribution is a minimum goal. Here’s how to ensure you don’t fall short:
- Check your savings each month.
- Use automatic transfers to your savings account.
- Adjust your lifestyle to meet the 20% savings goal.
- Remember, savings protect your future.
By avoiding these common mistakes, your 50/30/20 budget will thrive. Stay disciplined, and watch your finances improve.

Credit: www.synchronybank.com
Tools To Implement The 50/30/20 Rule
Managing money is easier with the right tools. The 50/30/20 budget rule helps many. It splits expenses into needs, wants, and savings. Let’s explore tools to make this budget work for you.
Budgeting Apps And Software
Technology makes budgeting simple. Several apps and software are designed for the 50/30/20 rule. They automatically categorize your spending. This helps you track your budget without stress.
- Mint: Tracks your spending and categorizes it.
- You Need A Budget (YNAB): Gives each dollar a job.
- Goodbudget: Uses envelopes to manage your finances.
These apps offer features like reminders, reports, and more. They keep you on track with your budget goals.
Spreadsheets And Manual Tracking
Some prefer a hands-on approach. Spreadsheets are perfect for this. They offer flexibility in tracking your budget. You can customize them to fit the 50/30/20 rule.
Create a spreadsheet with columns for needs, wants, and savings. Then, track your monthly expenses in each category. This method requires more effort but offers full control over your budget.
- Decide on a spreadsheet program (e.g., Excel, Google Sheets).
- Create categories for needs, wants, and savings.
- Regularly input your spending and income.
- Adjust as needed to stick to the 50/30/20 rule.
Whether you choose an app or spreadsheet, the key is consistency. Regular tracking leads to successful budgeting.
Success Stories: Testimonials And Outcomes
Many people dream of financial freedom. The 50/30/20 budget rule can turn this dream into reality. Let’s dive into real success stories. These people used the 50/30/20 rule wisely. Their lives changed for the better.
Debt Reduction Triumphs
Meet Emily. She was deep in credit card debt. Emily started using the 50/30/20 rule. She focused on her needs first. Then, she cut unnecessary wants. Soon, she put more money towards her debts. In two years, Emily was debt-free. Her credit score improved too.
John had student loans. He felt overwhelmed. The 50/30/20 rule was his game-changer. John lived more simply. He used extra cash to pay off loans. Now, John enjoys a debt-free life.
Achieving Financial Independence
- Lisa’s Journey: Lisa wanted to retire early. She saved 20% of her income. She invested it wisely. After ten years, Lisa reached financial independence.
- Mark’s Milestone: Mark dreamed of starting a business. He used the 50/30/20 rule to save. Mark collected enough money. He launched his own company successfully.
These stories inspire us. They show the 50/30/20 rule works. It brings financial wins. You too can achieve similar success. Start planning your budget today!
Conclusion: Empowering Your Financial Journey
Mastering the 50/30/20 budget rule can transform your finances. This simple yet powerful tool offers clarity. It guides your spending. It also nurtures healthy financial habits.
Recap Of Key Takeaways
The 50/30/20 rule splits income into three parts:
- 50% for needs
- 30% for wants
- 20% for savings
Let’s revisit the examples:
| Category | Monthly Income: $3000 |
|---|---|
| Needs ($1500) | Rent, groceries, utilities |
| Wants ($900) | Dining out, hobbies |
| Savings ($600) | Emergency fund, retirement |
Encouragement To Start Budgeting
Begin your budget journey today. Take control of your money. Enjoy peace of mind. Remember, small steps lead to big changes. Start with your next paycheck. Apply the 50/30/20 rule. Watch your savings grow. Build the life you envision.
Credit: intentionalaccounting.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is An Example Of The 50-30-20 Rule?
The 50-30-20 rule suggests allocating your after-tax income as follows: 50% for needs, 30% for wants, and 20% for savings or debt repayment. For instance, with a $3,000 monthly income, you’d use $1,500 for essentials, $900 for personal desires, and $600 for savings.
How Do You Distribute Your Money When Using The 50 20 30 Rule?
Allocate 50% of your income to necessities like housing and groceries. Set aside 20% for savings and debt repayment. Use the remaining 30% for discretionary expenses such as dining and entertainment.
What Is One Negative Thing About The 50-30-20 Rule Of Budgeting?
One downside of the 50-30-20 budgeting rule is its lack of flexibility for varying financial situations, potentially making it impractical for those with fluctuating income or high debt levels.
Why Is The 50/30/20 Rule Effective?
The 50/30/20 rule is effective because it simplifies budgeting. It allocates 50% of income to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings. This clear division helps people manage finances easily, ensuring essential expenses are covered while also promoting savings and discretionary spending.
Conclusion
Embracing the 50/30/20 budget rule can revolutionize your finances. This straightforward strategy simplifies money management, as we’ve seen through practical examples. Remember, 50% covers necessities, 30% goes to wants, and 20% is for savings. Start applying these principles today, and watch your financial health steadily improve.
Take control of your budget, and let your money work for you.